Great geniuses of humanity

Source: listas.20minutos.es
Geniuses who have marked our history, each specialist in their respective areas votes for the one you think is the best or the one you like the most. Do not forget to comment on the reason for your vote and whether or not you would like to have the ingenuity of one of them.
TOP 40:
Torrichelli

Italian physicist and mathematician whose contribution to physics has been considered one of the most important, is the author of the theorem that bears his name.
TOP 39:
Robert hooke
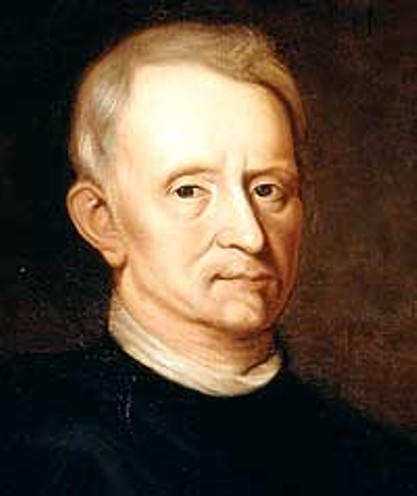

He was one of the most important experimental scientists in the history of science, tireless polemicist with a creative genius of the first order. His interests covered fields as diverse as biology, medicine, chronometry, planetary physics, deformable solids mechanics, microscopy, nautical and architecture. He created a microscope with which he could discover the cell
TOP 38:
George whashington

Military who was the first President of the United States (1789 - 1797) and Commander in Chief of the Continental Army of the revolutionary forces in the United States War of Independence (1775–1783). Washington began winning trophies, assembling troops from Virginia (United States) to support the British Empire during the Franco-Indigenous War (1754–1763), a conflict he inadvertently helped initiate. His military strategies helped his country achieve many things.
TOP 37:
Chio Hippocrates

He founded a school of Geometry, laid the foundations of the reduction method, that is, to transform a problem into another already solved. He began the use of letters in geometry figures.
TOP 36:
William Thomson (Lord Kelvin)

He was a British physicist and mathematician. Kelvin noted for his important work in the field of thermodynamics and electronics thanks to his deep knowledge of mathematical analysis. He is one of the scientists who did the most to bring physics to its modern form. He is especially famous for having developed the Kelvin temperature scale. He received the title of Baron Kelvin in honor of the achievements made throughout his career.
TOP 35:
Pierre Fermat

French mathematician whom Pascal called "the first brain in the world", can be considered as the greatest mathematician of the seventeenth century, formulated the famous theorem that bears his name.
TOP 34:
Jhon Dalton

He was a naturalist, chemist and mathematician, British meteorologist. He was the creator of the famous theory that bears his name, a fundamental contribution to chemistry.
TOP 33:
Claudio Ptolemy

The most outstanding of the astronomers of the Hellenistic era. He was one of the founders of trigonometry.
TOP 32:
Antoine Lavoisier

He is considered the father of modern chemistry for his detailed studies on: the oxidation of bodies, the phenomenon of animal respiration and its relationship with oxidation processes, air analysis, use of the balance to establish quantitative relationships in chemical reactions establishing its famous law of conservation of mass, studies in calorimetry, etc.
TOP 31:
Christopher Columbus

He was a navigator, cartographer, admiral, viceroy and governor general of the Indies in the service of the Crown of Castile, famous for having made the so-called discovery of America, in 1492.
TOP 30:
Euclid

He was the forerunner of our current Universities, he was also able to study nature without observing it, it was based solely on deductive calculations, he has formulated abstract general principles, that is, more important axioms for mathematics.
TOP 29:
Kant

He is considered one of the most influential thinkers in modern Europe and the last period of the Enlightenment. At present, Kant continues to have plenty of validity in various disciplines: philosophy, law, ethics, aesthetics, science, politics, etc.
TOP 28:
Voltaire

He was a French writer and philosopher who figures as one of the main representatives of the Enlightenment, a period that emphasized the power of human reason, of science and respect for humanity.
TOP 27:
Rutherford
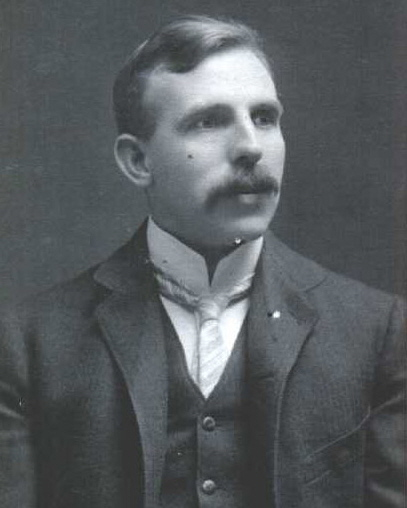

He is considered the father of nuclear physics. He studied the radioactive emissions discovered by H. Becquerel, and managed to classify them in alpha, beta and gamma. He found that radioactivity was accompanied by a disintegration of the elements, which earned him the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1908. He is owed an atomic model, with which he proved the existence of the atomic nucleus, in which all the positive charge and almost the entire mass of the atom. He achieved the first artificial transmutation with the collaboration of his disciple Frederick Soddy.
TOP 26:
Pedro Paulet

He was a Peruvian engineer, pioneer of Astronautics and Space Age. The scientist Wernher von Braun considers him, "The father of modern rocketry"
TOP 25:
Benjamin Franklin

He was an American politician, scientist and inventor. He enunciated the Principle of conservation of electricity. His most outstanding scientific work, Experiments and observations on electricity, was born from his studies. In 1752 he carried out his famous experiment with the kite in Philadelphia. He tied a kite with a metal skeleton to a silk thread, at the end of which he also had a metal key. By blowing it up on a stormy day, he confirmed that the key was charged with electricity, thus demonstrating that clouds are charged with electricity and lightning strikes are electric shocks. Thanks to this experiment he created his most famous invention, the lightning rod
TOP 24:
Napoleon Bonaparte

He was a French military and ruler, republican general during the Revolution and the Directory, architect of the coup d'etat of Brumaire 18 that made him First Consul. For a period of just over a decade, he acquired control of almost all of Western Europe and Central by conquests or alliances. Napoleon is considered one of the greatest military geniuses in history, having commanded very successful war campaigns, although with certain defeats equally loud
TOP 23:
Blas Pascal
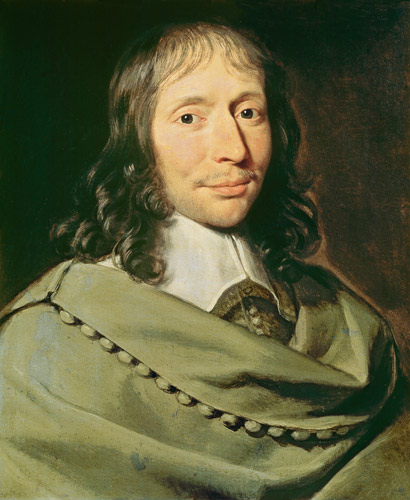

Child prodigy, showed his love of mathematics from his earliest age. I get to discover only 32 of Euclid's propositions, exposed in the "Elements", at 16 he wrote an "Essay on conics". He is the initiator of modern Geometry methods.
TOP 22:
Thales of Miletus
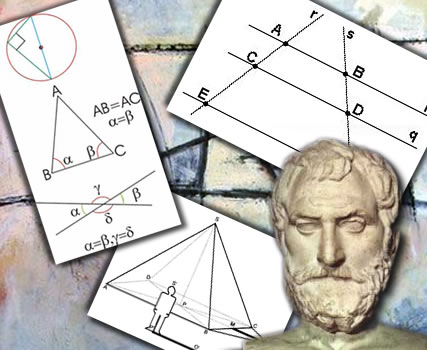
It was the first Greek geometer and one of the seven wise men of Greece. He had as a disciple and protected Pitagoras. In the illustration, some axioms shown by him are graphically shown: The sum of the 3 angles of a triangle is = two straight lines or 180º. The opposite angles of the vertex are equal.
TOP 21:
Discards
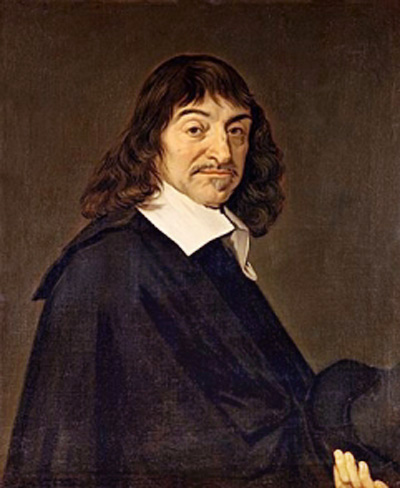

He is considered the Pioneer of Modern Philosophy and the creator of the notion of subject. In 1935 it was decided in his honor to call a lunar crater «Descartes».
TOP 20:
Karl Marx

He was a philosopher, historian, sociologist, economist, writer and German socialist thinker. Theoretical father of scientific socialism and communism, along with Friedrich Engels, is considered a key historical figure to understand society and politics.
TOP 19:
Shakespeare
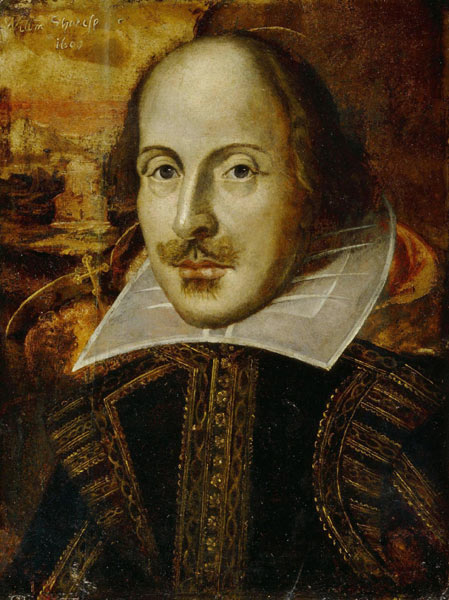

Known on occasion as the Bard of Avon (or simply The Bard), Shakespeare is considered the most important writer in the English language and one of the most famous of universal literature. The New Encyclopædia Britannica notes that "many consider him the greatest playwright of all time. His pieces are represented more times and in greater number of nations than those of any other writer."
TOP 18:
Pasteur
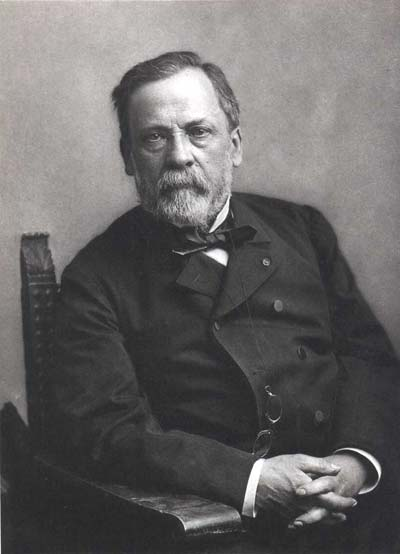

He was a French chemist whose discoveries were of great importance in various fields of natural sciences, especially in chemistry and microbiology. The technique known as pasteurization is due to him. He discovered the rabies vaccine, he is considered the father of microbiology.
TOP 17:
Nicolaus Copernicus

He was the astronomer who formulated the first heliocentric theory of the Solar System. His book, "De revolutionibus orbium coelestium" (of the revolutions of the celestial spheres), is usually conceived as the starting point or founder of modern astronomy, in addition to being a key piece in what was called the Scientific Revolution at the time Renaissance. Copernicus spent about twenty-five years working on the development of his heliocentric model of the universe.
TOP 16:
Archimedes

He was the most scientific of all Greek sages. His starting point was nature, he studied the curvilinear areas and the volumes of the bodies limited by curved surfaces that he applied to the circle, parabolic segment, spherical segment, cylinder, cone, sphere, etc. I believe the famous theorem that bears his name which is widely used in hydrostatics.
TOP 15:
Plato

It is who determined much of the corpus of central beliefs of both Western thought and ordinary man (what we now call "common sense" of Western man) and proof of this are the notion of "Truth" and the division between "doxa" ( opinion) & "episteme" (science), demonstrated or created and popularized (according to the perspective from which it is analyzed) a series of common ideas for many people.
TOP 14:
Thomas Edison

He was an important inventor who patented more than a thousand inventions, contributed to give the world contemporary technological profiles.
TOP 13:
Socrates

Fundamental representative of Greek philosophy, had great influence on Western thought, was a precursor to Plato and Aristotle.
TOP 12:
Mahatma Gandhi

His life, facts and thoughts demonstrated the value of self-management, social responsibility and pacifism as a form of revolution. His philosophy of socialpacifism teaches us today the value of working with others, for others and for others as a way to achieve peace, social justice and equality among all human beings.
TOP 11:
Pythagoras

He was a Greek philosopher and mathematician, famous above all for the Pythagorean Theorem
TOP 10:
Charles Darwin
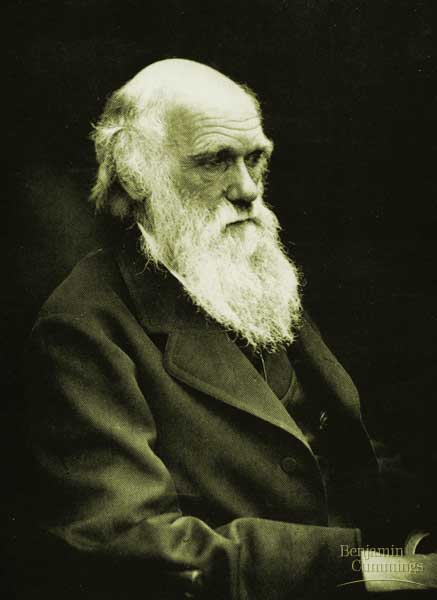

He was an English naturalist who postulated that all species of living beings have evolved over time from a common ancestor through a process called natural selection.
TOP 9:
Ludwig van Beethoven
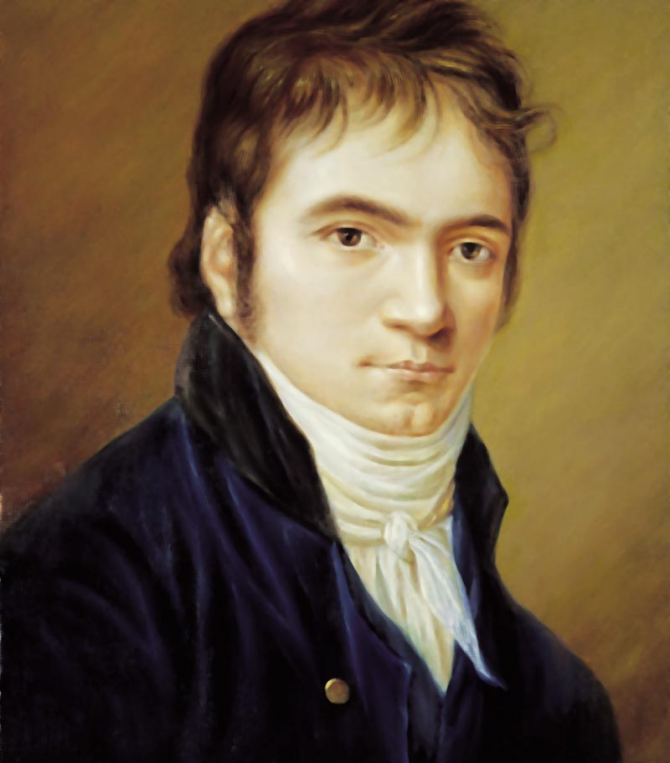

He was a composer, conductor and German pianist. His musical legacy extended chronologically from the classical period to the beginning of musical romanticism. Beethoven managed to transcend the music of romanticism, motivating its influence in a diversity of musical works throughout the nineteenth century. His art was expressed in numerous genres and although symphonies were the main source of his international popularity, his impact proved to be mostly significant in his works for piano and chamber music.
TOP 8:
Aristotle

He is one of the greatest philosophers of antiquity, in the history of Western philosophy and the most portentous encyclopedic author that humanity has given. He was the creator of formal logic, economics, astronomy, precursor of anatomy and biology and a creator of taxonomy (he is considered the father of zoology and botany).
TOP 7:
Galileo Galilei

He was an astronomer, philosopher, mathematician and physicist who was closely related to the scientific revolution. Eminent Renaissance man, he showed interest in almost all sciences and arts (music, literature, painting). His achievements include the improvement of the telescope, a great variety of astronomical observations, the first law of the movement and a decisive support for Copernicanism.
TOP 6:
Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart

He was a classical composer considered one of the greatest in his genre. Although he died very young (35 years), he left an extensive work that covers all the musical genres of his time, coming to compose more than 600 works, mostly recognized as the top works of symphonic music, concerted, of chamber, for piano, operatic and choral. He is also one of the most popular classical composers. In his earliest childhood in Salzburg, Mozart showed a prodigious ability to play the keyboard and violin, in addition to composing works at the age of five and performing interpretations for European royalty.
TOP 5:
Stephen Hawking

He is a physicist, cosmologist and science popularizer of the United Kingdom Among the many distinctions that have been granted to him, Hawking has been honored with twelve honorary doctorates and has been awarded the Order of the British Empire (ECB degree) in 1982, with the Prince Award of Asturias de la Concordia in 1989 and with the Copley Medal in 2006
TOP 4:
Isaac Newton

He was an English physicist, philosopher, inventor, alchemist and mathematician, author of the Philosophiae naturalis principia mathematica, better known as the Principia, where he described the law of universal gravitation and established the foundations of Classical Mechanics through the laws that bear his name. Among his other scientific discoveries are the works on the nature of light and optics (which are presented mainly in the Opticks) and the development of mathematical calculation. Newton was the first to demonstrate that the natural laws that govern the movement on Earth and those that govern the movement of the celestial bodies are the same.
TOP 3:
Nicholas Tesla

He was a physicist, mathematician, electrical engineer and famous inventor [1] who revolutionized electrical theory by developing the bases for the generation of alternating current.
TOP 2:
Leonardo da Vinci

He was an architect, sculptor, painter, inventor, musician, engineer and the Renaissance man par excellence. Frontline humanist, he is widely regarded as one of the greatest painters of all time and perhaps the person with the most varied talents in history. [1]
TOP 1:
Albert Einstein

He was a physicist of German origin, later Swiss and American nationalized. He is the best known and considered the most important scientist of the twentieth century. In 1905, being a young unknown physicist, employed at the Bern Patent Office (Switzerland), he published his Theory of Special Relativity. It incorporated, in a simple theoretical framework, based on simple physical postulates, concepts and phenomena previously studied by Henri Poincaré and Hendrik Lorentz. Probably, the most popular physics equation at the popular level is the mathematical expression of mass-energy equivalence, E = mc², deduced by Einstein as a logical consequence of this theory. That same year he published other works that would lay some of the foundations of statistical physics and quantum mechanics. In 1915 he presented the General Theory of Relativity, in which he completely reformulated the concept of gravity. One of the consequences was the emergence of the scientific study of the origin and evolution of the Universe by the branch of physics called cosmology.












