Shark classes
|
NEWS

Source: listas.20minutos.es
Some of them are very large, while others are quite small. Some are feared, while others are very calm and only care about their own business. You might be surprised that some of the giant sharks in the ocean are the friendliest you can find. There are more than 360 different species or types of sharks in the world, classified in 8 different orders.
TOP 36:
Milky Shark

The milky shark, Rhizoprionodon acutus, is a species of shark of the Carcharhinidae family, whose common name comes from an ancient Hindu belief, that the consumption of its meat promotes breastfeeding in newly born mothers. The milky shark typically measures 1.1 m (3.6 feet) long, and can be found in tropical coastal waters of the eastern Atlantic and the Indo-Pacific.
TOP 35:
Mielga shark

Myelga, galludo or chubby tollo (Squalus acanthias) is a species of squalid elasmobranch of the Squalidae family. It is a small shark of approximately one meter in length and stylized body with poisonous spines and very affiliated in the dorsal fins. Myelga is ovoviviparous, with litters of 1 to 20 embryos per pregnancy. Generally, large females have more numerous litters and young that reach a larger size at birth. The young measure between 22 and 33 cm. at birth and the sex ratio is the same. The female releases the embryos through the head with a series of rhythmic contractions reminiscent of birth in mammals.
TOP 34:
Shark Horn

The horned suño (Heterodontus francisci) is a species of heterodontiform elasmobranch of the Heterodontidae family. It is a small shark that can reach a size of 122 cm and is brown with black dots. Distribution and habitat of the horn shark It is found in central California, in the Sea of Cortez, Mexico, and probably also in Ecuador and Peru.
TOP 33:
Pygmy shark

The pygmy shark, Euprotomicrus bispinatus, the second smallest of all shark species after the dwarf tollo, is a shark from the Dalatiidae family, the only member of the genus Euprotomicrus. Its length is up to about 25 cm (10 inches) for females and about 22 cm (8.7 inches) for males.
TOP 32:
Bamboo shark

The bamboo shark (Hemiscyllidae) is a shark of the family of the oretobliformes, they are found in the Indo-Pacific area. They are small sharks that do not measure more than 121 cm.
TOP 31:
Bullet Shark or Silver Shark
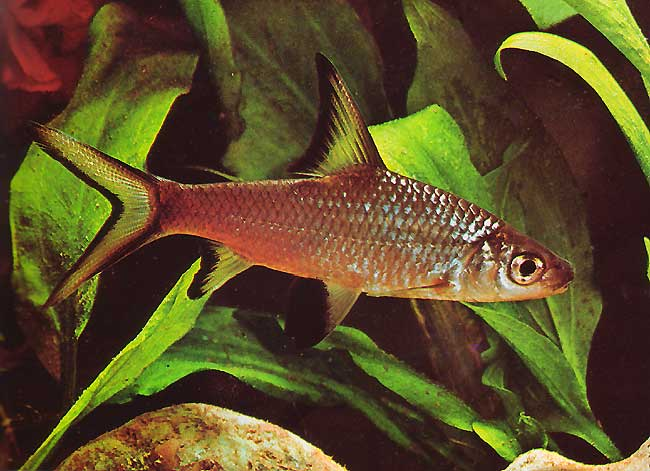

The silver shark or tricolor shark or bullet shark (Balantiocheilus melanopterus) is a species of fish in the Cyprinidae family, and has long been considered the only member of the genus Balantiocheilus. This species is not a strictu sensu shark, but it is commonly called "shark" because of its similar shape and large fins. It is native to Southeast Asia. It is oviparous, although it is not very likely that it can reproduce it in captivity.
TOP 30:
Shark angel

Squatina is a genus of selacimorph elasmobranchs, the only one of the Squatinidae family and of the order Squatiniformes, which includes those commonly known as angels or angel sharks. They have a flat body and broad pectoral fins, they make it similar to the line (order Rajiformes), although they are really sharks.
TOP 29:
Aquarium sharks

A shark may be something that is never considered as an animal that people should have in an aquarium, but the fact is, that different types of sharks are kept in domestic aquariums around the world. Saltwater aquarium sharks are usually small sharks, such as reef sharks. There are also a number of popular freshwater fish that are known as "freshwater" aquarium sharks. These species are not true sharks, and do not even relate to sharks. However, there are "true" freshwater sharks, although they are rare and not readily available in the aquarium trade.
TOP 28:
Shark Cat

The copper shark (Carcharhinus brachyurus) is a species of carcharriniform elasmobranch of the Carcharhinidae family that inhabits most of the world's oceans with warm or temperate waters.
TOP 27:
White tip reef shark
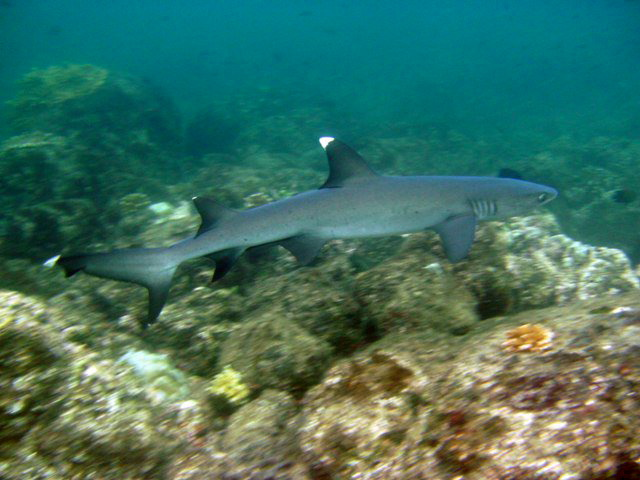

The white tip shark, Triaenodon obesus, is a species of shark of the Carcharhinidae family and the only member of its genus. A small shark, usually not exceeding 1.6 m (5.2 feet) in length, this species is easily recognizable by its thin and short body, but wide head, as well as tubular skin flaps next to the nose, oval eyes, with vertical pupils and white tip dorsal and caudal fins. One of the most common sharks found in Indo-Pacific, coral reefs, the white tip shark is distributed west to South Africa and east to Central America. They are usually found at or near the bottom in clear waters, at a depth of 8-40 m (26-130 feet).
TOP 26:
Copper Shark

The copper shark (Carcharhinus brachyurus) is a species of carcharriniform elasmobranch of the Carcharhinidae family that inhabits most of the world's oceans with warm or temperate waters.
TOP 25:
Dog shark

There is little knowledge about aspects of the dog shark species, sharks of that family mainly consume fish, crustaceans and cephalopods; It is also established that they are ovoviviparous. The maximum length reached by individuals of this species of dog shark is 500 millimeters; females are larger, easily reaching the maximum size, adult males usually do not exceed 400 mm in length. The dog shark is a species of deep depth, it has little knowledge; of its life parameters (feeding, reproduction, behavior). Species have been reported in the seas of Panama, the tropical Pacific, in front of Central America and in the area of Hawaii and Chile, north-central zone.
TOP 24:
Spear shark

The largest known male and female spear shark in the log was 1.6 m and 1.8 m long, respectively, suggesting a maximum length of 2.5 to 3 m of adults. The spear shark has a streamlined body, more robust with a short and wide head. The snout is flattened, with a large nose divided into the openings and incurrent and excursion by large, triangular flaps of the skin. The eyes are small and equipped with nictitating membrane (third protective eyelid). The large arc-shaped mouth has very little grooves in the corners. There are 26-29 and 27-29 upper and lower rows of teeth. The teeth are tall and straight, those of the upper jaw are wide and triangular with serrated edges, while those of the lower jaw narrow and like spears with teeth only near the tip, and small small cusps at the base in individuals very young There are five pairs of gill slits, with the first pair larger than the others.The large pectoral fins have large margins behind the main ones, and blunt tips. The pelvic fins are triangular, with almost straight margins
TOP 23:
Bocagrande shark

Its body is sharp, flaccid, blackish brown and, as the name implies, it has a huge, rounded mouth, and with a group of small circular spots on the “lip” of the lower jaw, luminescent organs that surely help you to attract food. His teeth are small and not functional. The maximum reported size is approximately 5.50 m. Males mature sexually at 4 m, while females at 5 m in total length.
TOP 22:
Leopard shark

Leopard shark It is a species of triad that lives along the North American Pacific coast from the US state of Oregon to Mazatlan in Mexico. With a body measurement between 1.2 and 1.5 m long, this slender body shark is easily identifiable by its striking pattern of marks and spots along its back, to which it owes its vulgar name. It usually has gray or brown coloration. Being predators of active swimming, groups of leopard sharks frequently follow the tide towards marshes formed in intertidal areas in search of food, mainly clams, worms, crabs, shrimp, bony fish and fish roe.
TOP 21:
Port Jackson shark
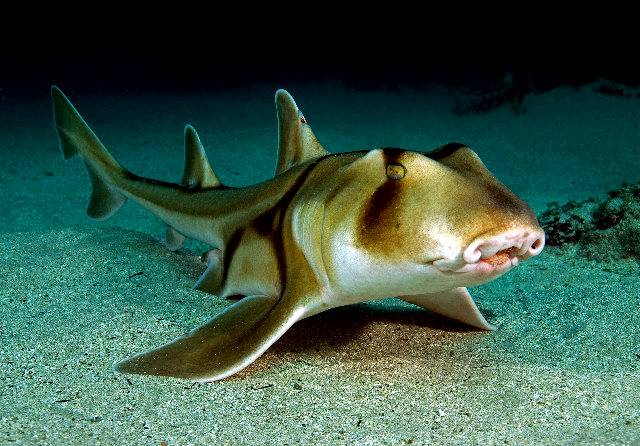

The scientific name of Heterodontus portusjacksoni comes from the Greek words "Heteros" - different and "dont" - tooth, and refers to the peculiar shape of the denture of this shark. "Portusjacksoni" comes from Port Jackson, which is the name that Sydney Harbor receives. The shark of Port Jackson is the largest of its family, the Heterodóntidos and can measure 1.65m, although commonly they are smaller, the males usually reach 75cm and the females between 80 and 95cm. At birth, Port Jackson shark pups, known as "pups" are about 25 centimeters in length.
TOP 20:
Gray shark

The gray shark (Carcharhinus amblyrhynchos) is a species of carcharriniform elasmobranch of the Carcharhinidae family. It is one of the most common sharks in the Pacific, from the Red Sea to Easter Island. They are usually 250 meters deep. There is also evidence of it near islands, coral or rocky regions. As the name suggests, its color is mostly gray, with a white bottom surface. The extremities of most fins, except the first dorsal fin, are darker, and the caudal fin has a prominent black margin. Some individuals have a white pattern on the main edge of the dorsal fin. The largest reach 2.55 m. It can easily be confused with the black reef shark, with the difference that it has the first black dorsal fin.
TOP 19:
Caribbean reef shark

The Caribbean reef shark, Carcharhinus perezi (often misspelled, perezii) is a species of requiem shark of the Carcharhinidae family. With a robust aerodynamic body typical of requiem sharks, this species is difficult to distinguish between other members of its family, such as the dark shark (C. obscurus) and the silky shark (C. falciformis). Distinctive features are the fins of dark color, without prominent marks, a short free rear tip on the second dorsal fin, as well as the shape of the tooth and its number.
TOP 18:
Carpet shark

Typical orectolóbido, wide body and very flattened, especially in the anterior half. The snout is wide, very depressed, with tiny eyes located in the dorsal position, large immediately adjacent spiracles, wide and terminal mouth endowed with re-cut dermal lobes, the two dorsal fins are very delayed and of similar dimensions. The dorsal coloration, very elegant and only apparently colorful, has broad dark markings bordered by black on a greenish or yellowish background, richly adorned by a myriad of lighter macules and labyrinth ornaments. They have curved modified teeth, both in the upper and lower jaw.
TOP 17:
Zebra shark
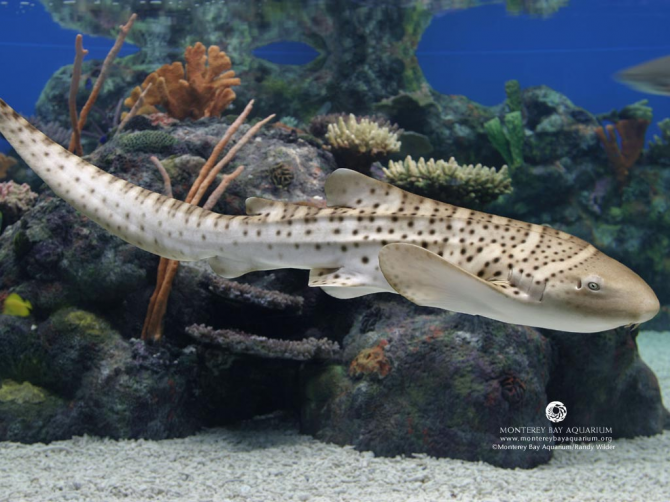

Appearance The zebra shark, whose caudal fin, or tail, is almost as long as the rest of the body, can measure up to 3.5 m (11.5 feet) long. Adults do not have the characteristic stripes of zebras, but young people do. Young zebra sharks are black with yellow stripes, while adults are yellowish brown with dark spots on the whole body and crests along the dorsal part, or loin. The nose or nose of zebra sharks is large, but its mouth is small. Chins hang from the nostrils and allow you to sniff your prey. The eyes are very small and are located on the sides of the head. The spiracles, or organs that carry water to the gills, are located just behind the eyes. Did you know…? The zebra shark is the only member of the Stegostomatidae family. The zebra shark is often confused with the leopard shark, a smaller shark that lives in cold waters.
TOP 16:
Black tip reef shark

The blacktip shark, Carcharhinus melanopterus, is a species of shark of the Carcharhinidae family, easily identifiable by the prominent black tips on its fins (especially in the first dorsal fin and caudal fin). They are among the most abundant sharks that inhabit the tropical coral reefs of the Indian and Pacific oceans, this species prefers shallow and coastal waters and its exposure the first dorsal fin is a common spectacle in the region. Most blacktip reef sharks are found on reef shelves and sandy floors, although they are also known for entering brackish and freshwater environments. This species normally reaches a length of 1.6 m (5.2 feet) long.
TOP 15:
Lemon Shark

It has a long thin body and a rounded snout. The first dorsal fin and pectoral fins are small. The colors always approach gray, and can be yellowish or greenish. Under the tip of the mouth has a dark spot that gives the name in English ("blacknose shark"). This black spot is more differentiated in young specimens. The average size is about 125 cm and the weight of 10 kg. Taking this as a standard, there have been cases of specimens that reached 2 meters in length. The size at birth is between 40 and 50 cm. Mature males measure between 95 and 105 cm in length, and mature females between 100 and 105 cm.
TOP 14:
Crocodile shark

The crocodile shark can be found all over the world in tropical waters from the surface to a depth of 590 m (1,940 feet). It performs a vertical migration, staying below a depth of 200 m (660 feet) during the day and rising at shallow water at night to feed. Normally it is only 1 m (3.3 feet) long, the crocodile shark is the smallest mackerel shark alive. They are distinguished by their elongated cigar-shaped body, with very large eyes and relatively small fins.
TOP 13:
Shark Sierra of the Bahamasa

The Sierra Shark of the Bahamas, Pristiophorus schroederi, is a Sierra Shark of the Pristiophoridae family, located in the central-western Atlantic Ocean between the Bahamas and Cuba, at depths between 400 and 1,000 m. These sharks are at least 80 cm long.
TOP 12:
Mako shark

The common maroon is a great shark with a fusiform, robust, solid and very hydrodynamic body. Its snout is conical and pointed and the mouth is large and narrow, U-shaped with broad diastemas separating the hemimandibles. The eyes are round, black and medium sized. Medium scapular fins, slightly rounded end. First dorsal medium and slightly rounded end, with its origin just behind the scapulars; Tiny second dorsal and anal, both facing. Large caudal fin with wide and crescent-shaped lobes, with the upper lobe slightly larger than the lower one. Large gill slits, 5 pairs in total. Peduncle caudal depressed and widened by large very long lateral keels. The teeth are large, broad cusp (in adults) and flexed, with smooth edges, the third upper tooth is tiny and inclined followed by diastema. It is dark blue on the back, lighter on the sides and pure white on the belly.
TOP 11:
Goblin Shark

It measures between 2 and 3 meters, with a maximum of 3.85 meters. The snout is shaped like a blade, very elongated and flattened, with small eyes and numerous long pointed front teeth; The jaw is long, narrow and can project ostensibly outward, but it is usually in perfect alignment with the head profile. The dorsal fins are small and rounded, like the pectorals: the anal fin and the pelvic fins are larger than the dorsal ones. The body is flaccid and compressed laterally; the coloration is white with pink shades on the trunk and bluish on the fins, but it quickly turns brown on the specimens taken from the water.
TOP 10:
Fox shark

The spectacled fox (Alopias superciliosus), also known as the Ojón fox, fox shark, rabon and rabudo, is a species of lamniform elasmobranch of the Alopiidae family that lives in the world's tropical oceans, at depths of 500 m. Its maximum length is 5 meters (more typically 3 to 4 m), with weights of up to 360 kg (common 160 kg). It is a large shark with huge eyes that can be easily distinguished, adapted to vision at great depths. Large and wide pectoral fins.
TOP 9:
Prehistoric shark
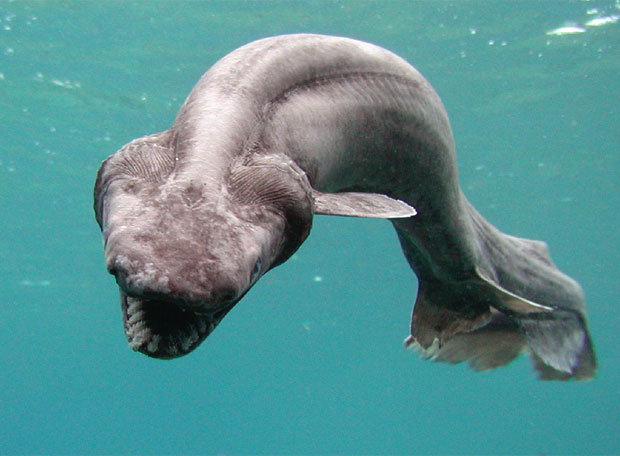

In the changing seas the Jurassic emerged the dawn of a new chapter in the history of the prehistoric shark. It was a period of great volcanic and tectonic activity that shook the foundations of Pangea, the great continent. The forces were not only destructive, they also created new possibilities. While the great mass of land was divided, the same divisions filled with water creating new seas. Shallow seas with lots of sunlight and lots of life. For millions of years the continents continued to divide and separate from each other. The seas became oceans that were gradually resembling the current ones. As the world modernized, so did prehistoric sharks and Ictiosaurs. The ancestors of the current shark species appeared in the Jurassic.
TOP 8:
Blue shark

The dyer is a stylized and elongated body shark, with a long, conical snout. It has large eyes that, like all carcarriniforms, are provided with a nictitating membrane, a kind of semi-transparent eyelid that goes from top to bottom and protects the eyeballs when fighting with their prey. It has five gill slits, two dorsal fins, two pectoral fins, two anal fins and a caudal fin. The pectoral fins are long and thin, and the caudal fin is provided with an upper lobe also very elongated. It has a white coloration in the ventral part, and a very intense metallic blue in the rest of the body. Their teeth, which fall and are constantly replaced, are triangular in shape with serrated edges. It has an average length of 2.5 m and a weight of 80 kg, although there have been cases of adult females with lengths greater than 4 m and weighing up to 220 kg. As a peculiarity, it should be noted that, given the length of his nose, his jaw has been adapted to bite without problems since the upper part of the jaw is able to project forward, so that to bite you do not need to lift your head.
TOP 7:
Basking shark
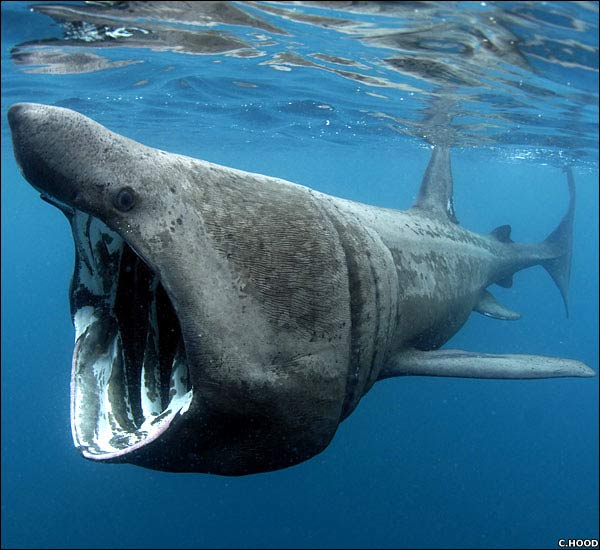

The basking shark (Cetorhinus maximus) is a species of carcharriniform elasmobranch of the Carcharhinidae family. It is the second largest fish in the world and reaches 10 meters in length and four tons in weight. Although its silhouette resembles that of a hunting shark, with a hydrodynamic shape and sharp snout, it feeds by filtering the water. Swim with your mouth open until it is round and filter the water through huge gills. It moves very slowly.
TOP 6:
Hammerhead shark

The most striking feature of all hammerhead shark species is the particular shape of the T-shaped head, with the eyes and nostrils located at the ends of the head, thanks to which the movement of head from side to side Swimming looks around everything around you and even what's left behind.
TOP 5:
Bull shark

It has a solid body with two large dorsal fins, and an elongated tail with a long upper lobe and a precaudal peak. It reaches up to 3.2 m in length. The average of the males is 2.1 m and that of the females 2.2 m. They have a gray and white background above. In August 2007, an albino specimen was photographed in South West Rocks, Australia.
TOP 4:
Whale shark
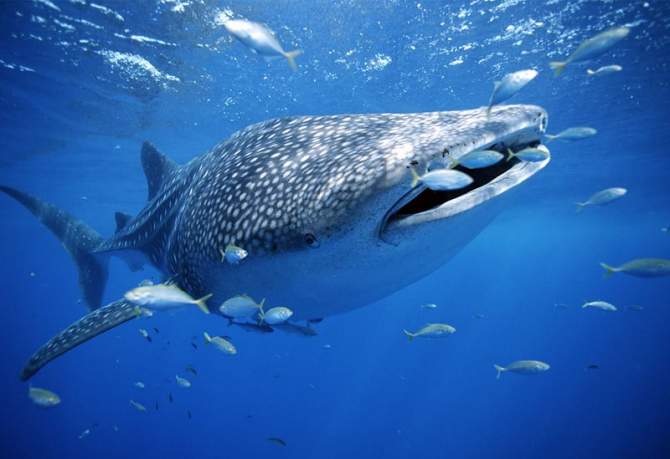

The whale shark inhabits the oceans and warm seas, near the tropics. They are believed to be pelagic fish, but in certain seasons they migrate long distances to coastal areas, such as Ningaloo Reef in Western Australia, Utila in Honduras, Donsol and Batangas in the Philippines, Holbox Island in Yucatan, Mexico, and the Pemba and Zanzibar Islands of Tanzania. Although it is common to find it offshore, it is also possible to spot it near the coast, entering lagoons or coral atolls, and near the mouths or estuaries of the rivers.
TOP 3:
Tiger shark
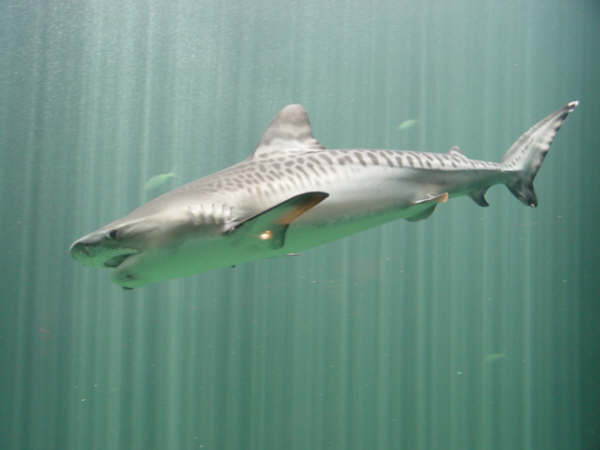

The last name of "tiger" is because, like the great Asian cat, this shark has a series of transverse dark stripes on the back and sides that tend to fade with age. The rest of the body is gray or light blue-green, being replaced by white on the face and the ventral area. The nose is flat and the head, quite crushed, has an almost rectangular shape, where a large parabolic mouth that is surrounded by very developed lip folds stands out. The eyes are large and circular and the nostrils elongated and very advanced, arranged almost in a frontal position. The teeth are large, sharp and very hooked, provided with strongly serrated edges, except in the inner part of the tip. This peculiar morphology makes them perfectly capable of breaking bones of large animals and shells of sea turtles. If one of the teeth is lost during the attack, another grows to take its place.
TOP 2:
megalodon shark

The megalodon carcharodon is a prehistoric creature that lived millions of years ago. It is believed that they existed in the period between 1.6 million to 5 million years ago, although some experts trace it even further. Officially, the Carcharodon megalodon is extinct. This extinction is relatively "recent" and even the accepted date is about a million and a half years ago, however, there have been indications that megalodons could have survived until just about 10,000 years ago, if this is true then it is a much smaller jump to believe that they could exist even.
TOP 1:
White shark
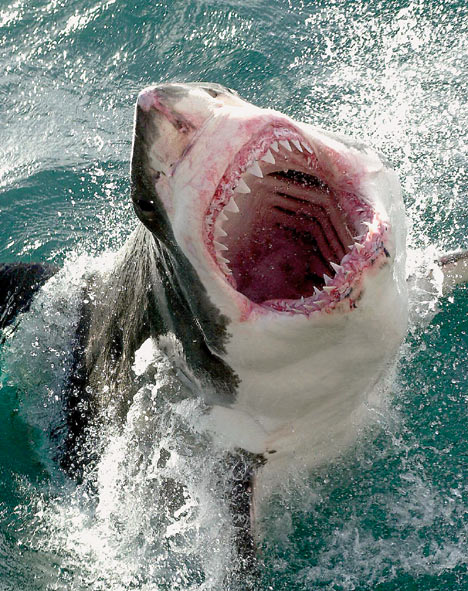

White sharks are characterized by their fusiform body and great robustness, in contrast to the crushed forms that other sharks usually wear. The nose is conical, short and thick. The mouth, very large and rounded, is shaped like an arc or parabola. Always remain ajar, revealing at least one row of teeth of the upper jaw and one or two of the lower, while the water penetrates into it and leaves continuously through the gills. If this flow stopped, the shark would drown because it lacked operculums to regulate the correct passage of water, and it would sink into it, since not having a swim bladder is condemned to be in continuous motion to avoid it.